Although preventing diabetes is the main advantage of eating with insulin and glucose in mind, there is growing evidence that maintaining blood sugar levels within the normal range can lead to better metabolic health, improved renal function, and a lower risk of developing several types of cancer. Achieving appropriate glucose levels doesn’t require drastically reducing carbohydrate intake or eliminating all grains.
To manage blood sugar effectively, focus on slowing carbohydrate digestion by consuming enough protein, fiber, and healthy carbohydrates.
Key Dietary Guidelines for Blood Sugar Management

- Consume Whole Foods: Minimize processed foods and emphasize nutrient-dense options.
- Eat a Lot of Color: Include colorful fruits and vegetables in your diet.
- Focus on Healthy Carbohydrates: Learn the role of carbs in energy production and cellular activity.
How Your Body Turns Food into Energy

Understanding how food affects your body is crucial for managing blood sugar. Here’s how your body processes carbohydrates:
- Digestion of Food:
Carbohydrates from sources like bread, rice, pasta, grains, beans, and lentils are broken down into glucose during digestion. Dairy products also contribute to your carb intake. - Glucose Absorption:
Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream through your gut after digestion. - Insulin Release:
Your pancreas detects the rise in blood glucose and releases insulin into the bloodstream. - Insulin and Cell Receptors:
Insulin binds to cell receptors, unlocking pathways for glucose to enter the cells. - Energy Production:
Glucose inside the cells is converted into energy, serving as the preferred fuel for your brain and muscles.
Savor Nutritious Carbs
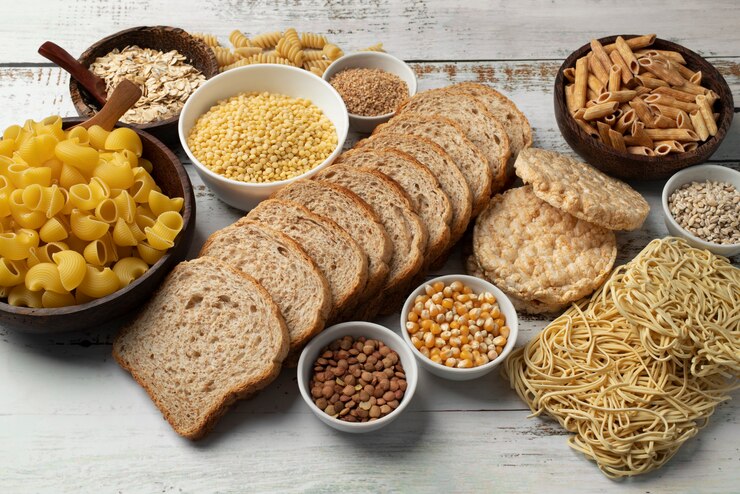

To maintain balanced blood sugar levels, prioritize these carbohydrate sources:
- Fruits: Berries, watermelon, cantaloupe, and honeydew melons.
- Vegetables: Especially green leafy vegetables and other non-starchy options (excluding corn, peas, and potatoes).
- Whole Grains: Opt for whole grain bread, rice, and pasta with high fiber content.
The Protein Factor

Protein, fat, and fiber digest more slowly, preventing rapid spikes in blood glucose. Pairing protein with carbohydrates allows glucose to enter the bloodstream gradually, keeping you fuller for longer.
Examples of Protein and Carb Pairings:
- A handful of almonds with fruit.
- A spoonful of peanut butter on whole-grain bread.
- A hard-boiled egg with a small serving of rice.
- Chicken or tofu alongside whole-grain pasta.
Fiber for the Win!
Fiber is essential for managing blood sugar levels. Choosing whole grains high in fiber for foods like pasta, rice, and bread helps prevent glucose spikes. Additionally, fiber supports gut health and heart health.
Fiber Goals:
- Daily Minimum: Aim for at least 25 g of fiber per day.
A Quick Recap
To naturally manage blood sugar, remember these points:
- Increase Your Fiber Intake: Strive for a minimum of 25 g daily.
- Balance Carbs and Protein: Pair carbs with protein at every meal or snack to stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Limit Processed/Refined Carbs: Aim to consume processed or refined carbs only 20% of the time, while 80% of your carbs come from whole foods.
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels doesn’t have to be complicated. By following these simple strategies and making thoughtful food choices, you can enhance your overall health while keeping your blood sugar in check.